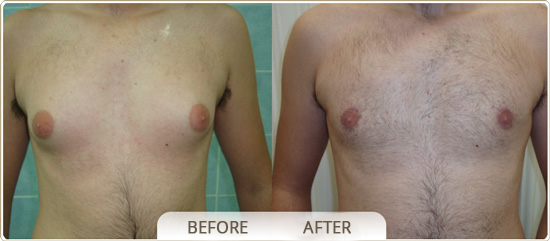
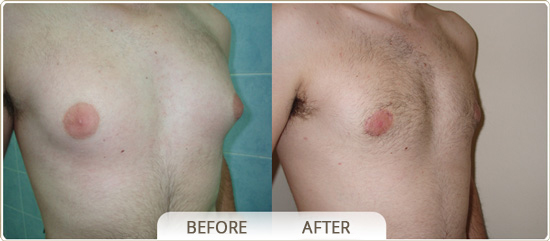
GYNECOMASTIA
Gynecosmastia is defined as the enlargement of the male breast and can be fairly common (estimates of 40% of the male population).
Gynecomastia often occurs in pubertal boys and can resolve on its own within 1-2 years. It constitutes in the enlargement of the gland tissue or the presence of fat deposits or both. Typically there are no symptoms like pain or feeling of pressure. Surgical removal is mainly performed due to psychological consequences.
Gynecomastia is mainly due to an imbalance in hormone levels (estrogen concentration is relatively high compared to the level of androgen). However the causes are multiple and include obesity, hereditary factors and certain of medical conditions. These can include lung cancer, liver disease, testicular tumors and hyperthyroidism. Certain medications can promote breast growth. For example, medication for depression, prostate cancer, cardiological diseases, diuretics, chemotherapeutics et al or substances of abuse (alcohol, marijuana, heroin) or anabolics.
The treatment of gynecomastia is by surgical resection. It is performed under a general anaesthesia and it removes the breast glandular tissue through a small semicircular incision on the lower skin – areola border. It can be combined with a liposuction in the surrounding area at the time of surgery. In certain cases, when gynecomastia is mainly due to deposits of fat tissues, then the liposuction surgery is all that is necessary. Excess skin, remaining after the removal of the gland, usually shrinks back on its own on young people. After surgery a dressing or compression garment is recommended to be used continuously for 20 days.